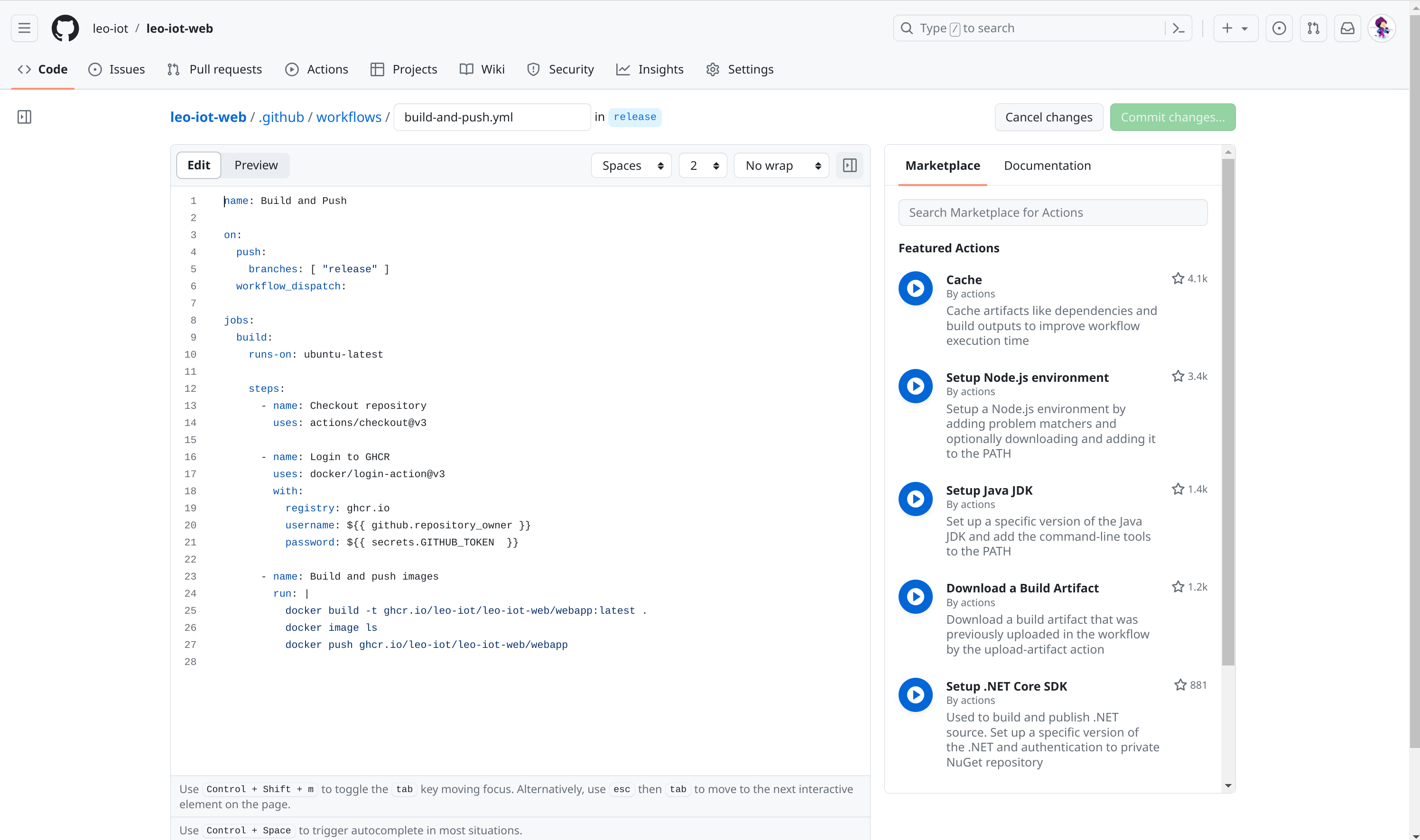
1. Mit der vm08 verbinden und ein Schlüsselpaar erstellen
ssh lsadmin@vm08.htl-leonding.ac.at ssh-keygen -t rsa
2. Den generierten privaten Schlüssel, den Benutzer, die URL und das Passwort in die GitHub-Secrets eintragen
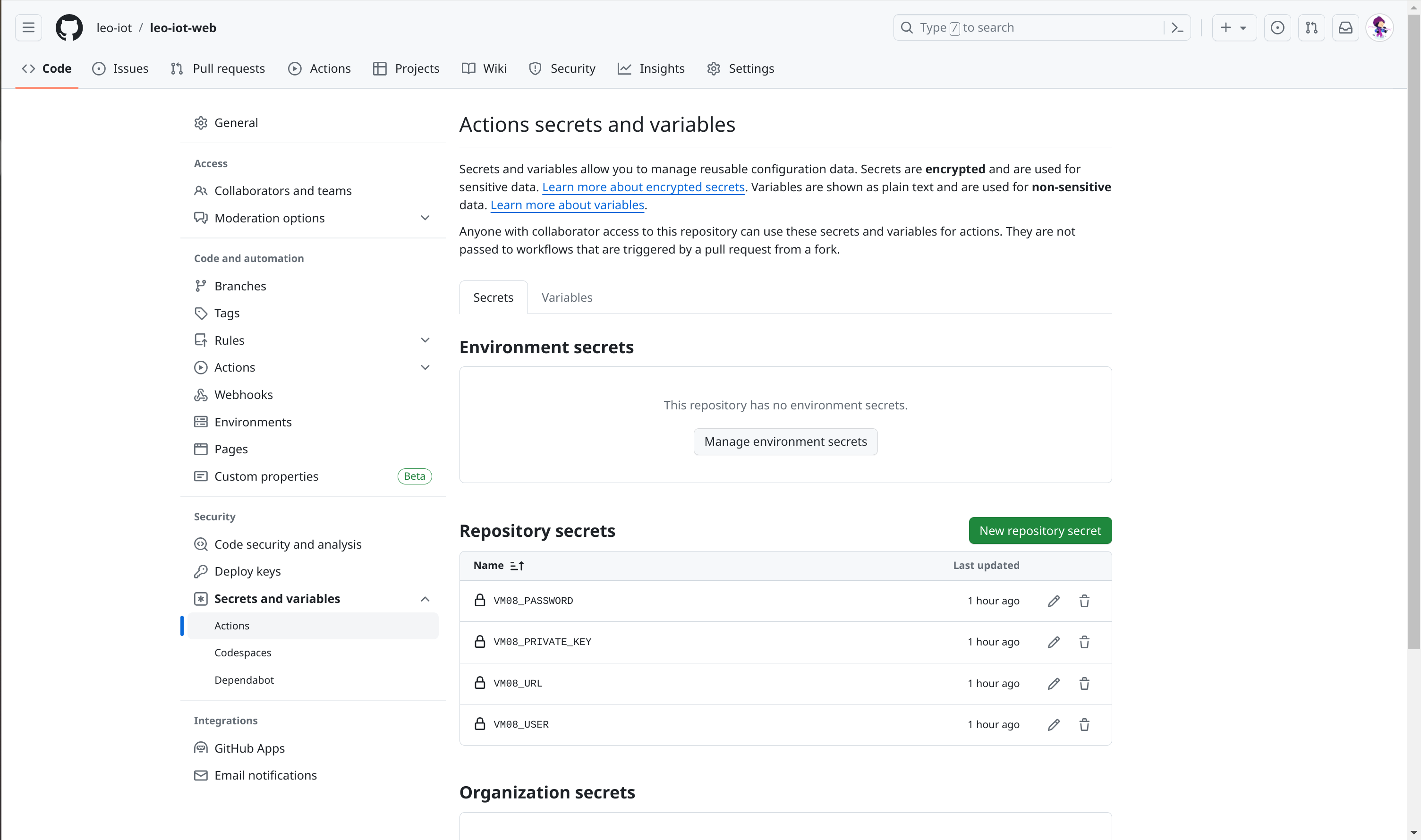
| Die URL ohne @ eintragen (vm08.htl-leonding.ac.at) |
3. GitHub Action
Configure klicken
3.1. Erklärung .yml File
build-and-push.yml
name: Build and Push
on:
push:
branches: [ "release" ]
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository (1)
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Login to GHCR (2)
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
registry: ghcr.io
username: ${{ github.repository_owner }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Build and push images (3)
run: |
docker build -t ghcr.io/leo-iot/leo-iot-web/webapp:latest .
docker image ls
docker push ghcr.io/leo-iot/leo-iot-web/webapp| 1 | Ohne den Checkout-Schritt hätten nachfolgende Schritte in dem Workflow keinen Zugriff auf die Codebasis, und man könnte keine Aktionen wie das Bauen, Testen oder Deployen der Anwendung durchführen. |
| 2 | Dieser Anmeldeschritt ist notwendig, bevor Docker-Images in GHCR hochgeladen werden, um sicherzustellen, dass der Workflow über die erforderlichen Anmeldedaten verfügt. |
| 3 | Baut ein Docker-Image aus dem angegebenen Dockerfile, taggt es mit der neuesten Version und lädt es in ein Docker-Registry hoch. |
4. Cronjob auf der vm08
Definiton: Ein Cronjob ist eine geplante Aufgabe, die regelmäßig zu bestimmten Zeitpunkten oder in festgelegten Intervallen automatisch ausgeführt wird.
4.1. docker-compose.yml
Im Ordner /opt/docker/leo-iot ein docker-compose.yml File erstellen.
version: '3.7'
services:
leo-iot-web:
depends_on: [ leo-iot-db, leo-iot-server ]
image: ghcr.io/leo-iot/leo-iot-web/webapp
container_name: leo-iot-web
ports:
- 80:80
networks:
- iot_net
leo-iot-server:
depends_on: [leo-iot-db]
image: ghcr.io/leo-iot/leo-iot-server/app
container_name: leo-iot-server
ports:
- 8080:8080 # the HTTP endpoint
extra_hosts:
- mqtt.htl-leonding.ac.at:10.191.112.90
networks:
- iot_net
restart: always
leo-iot-db:
image: ghcr.io/leo-iot/leo-iot-database/app
container_name: leo-iot-database
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: app
POSTGRES_USER: app
POSTGRES_DB: db
volumes:
- ./data/:/var/lib/postgresql/data
ports:
- 5432:5432
networks:
- iot_net
networks:
iot_net:
ipam:
driver: default
config:
- subnet: 10.139.0.0/164.2. docker-cronjob.sh im Home-Verzeichnis erstellen
#!/bin/bash
# Wechsle zum Verzeichnis, in dem sich die docker-compose-Datei befindet
cd /opt/docker/leo-iot
# Stoppe laufende Container
docker-compose down
# Starte Container neu
docker-compose up -d4.4. Cronjob konfigurieren
crontab -e
# Edit this file to introduce tasks to be run by cron.
#
# Each task to run has to be defined through a single line
# indicating with different fields when the task will be run
# and what command to run for the task
#
# To define the time you can provide concrete values for
# minute (m), hour (h), day of month (dom), month (mon),
# and day of week (dow) or use '*' in these fields (for 'any').
#
# Notice that tasks will be started based on the cron's system
# daemon's notion of time and timezones.
#
# Output of the crontab jobs (including errors) is sent through
# email to the user the crontab file belongs to (unless redirected).
#
# For example, you can run a backup of all your user accounts
# at 5 a.m every week with:
# 0 5 * * 1 tar -zcf /var/backups/home.tgz /home/
#
# For more information see the manual pages of crontab(5) and cron(8)
#
# m h dom mon dow command
0 2 * * * /home/lsadmin/docker_cronjob.sh (1)| 1 | Das sh-File wird nun jeden Tag um 2 Uhr in der Früh ausgeführt |